B-The association of multiple polypeptides. The tertiary structure of a protein refers to the arrangement of amino acid side chains in the protein.
Solved Question 21 Points Which Of The Following Best Chegg Com
Make sure you know the secondary structures that make up the tertiary structures.
. At this level every protein has a specific three-dimensional shape and presents functional groups on its outer surface allowing it to interact with other molecules and giving it its unique function. The three dimensional structure of a protein due to the spatial arrangement of the side chains of the amino acids. The type of side chain on the amino acid determines the.
Hydrogen bonding between side-chains contributes to protein tertiary structure but not secondary structure. The arrangement is made with the help of chap. Which of the following statements best describes the tertiary structure of a protein.
The tertiary structure is the final specific geometric shape that a protein assumes. The structure formed from interactions between the amino acid side groups. It includes alpha helices as a common form.
Tertiary structure of a protein describes A The order of amino acids B Location of. This important principle of biochemistry was first determined by the biochemist Christian Anfinsen in studies of the enzyme ribonuclease. H-bonds electrostatic forces disulphide linkages and Vander Waals forces stabilize this structure.
Tertiary protein domains are formed by combinations of disulfide bonds hydrogen bonds ionic bonds and non-polar hydrophobic interactions. Best answer D The ways of protein folding. This is what we call the tertiary structure of proteins.
The tertiary structure of a protein are formed by coiling and folding of chains of proteins which are held together by the weak non-covalent interacting formed between various parts of the polypeptide chain. The three-dimensional structure of a protein is called Tertiary Structure. This is the structure that gives protein the 3-D shape and formation.
C-The linear sequence of amino acids making up the polypeptide. They are usually stable but do not conform to any frequently recurring pattern. The R-group of the last.
After the amino acids form bonds secondary structure and shapes like helices and sheets the structure can coil or fold at random. Tap card to see definition. The hydrogen bonds in the secondary and tertiary structure of proteins are directly attacked by.
The polypeptide chain can experience additional foldings to produce the tertiary structure. These binding interactions may be stronger than the hydrogen bonds between amide groups holding the helical structure. It involves hydrogen bonding between amino acid side- chains.
Hemoglobin is a globular protein composed of a single polypeptide chain that has one O 2 binding site. Tertiary Structure refers to the comprehensive 3-D structure of the polypeptide chain of a protein. The forces that stabilize these contacts are mainly the contacts between the side chains of the amino acids but occasionally hydrogen bonds of the polypeptide chain can participate.
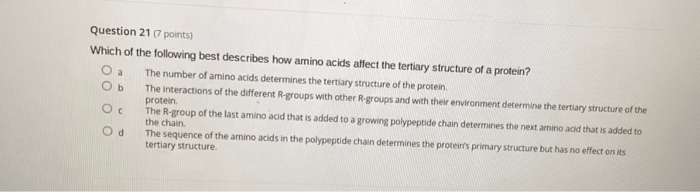
Question 3 Which of the following best describes how amino acids affect the tertiary structure of a protein. This final shape is determined by a variety of bonding interactions between the side chains on the amino acids. Asked Oct 22 2019 in Biology by Shivam01 820k points.
It includes beta pleated sheets as a common form. Describe The Tertiary Structure Of Proteins. What Is Meant By Tertiary Structure Of Proteins.
Tertiary Structure of Protein This structure arises from further folding of the secondary structure of the protein. The tertiary structure consists of eight beta-strands connected by α-helices known as the globin fold Hemoglobin is a tetramer composed of two different types of globin subunits each of which has an O 2 binding site. A-Characteristic patterns such as helices and sheets that arise when hydrogen bonds form between the amino acids of polypeptides.
There are several types of bonds and forces that hold a protein in its tertiary structure. The tertiary structure of a protein refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of its polypeptide chain in space. Fibrous mainly 4 types.
The tertiary structure is created by several types of bonds between the amino acids. Keratin two right handed coils to make a left. A The tertiary structure of a protein is the folded structure alpha-helix or beta-sheet formed by additional bonds that are formed in the polypeptide chain.
The tertiary structure of proteins represents overall folding of. For example the hormone insulin has two polypeptide chains A and B shown in diagram below. The interactions of the different R-groups with other R-groups and with their environment determine the tertiary.
It involves hydrogen bonding between the backbone atoms. The tertiary structure of a protein is the set of angles contacts and conformations of all the atoms of a polypeptide chain that give rise to the folding of said polypeptide. Alpha helix and beta sheets are the major secondary structures of a protein.
Which of the following statements describes the tertiary structure of a protein. The tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. For instance in globular proteins the polypeptide chains are held together in a definite way forming a compact structure.
Of proteins D The ways of protein folding. They are strongly influenced by side chain groups. The number of amino acids determines the tertiary structure of the protein.
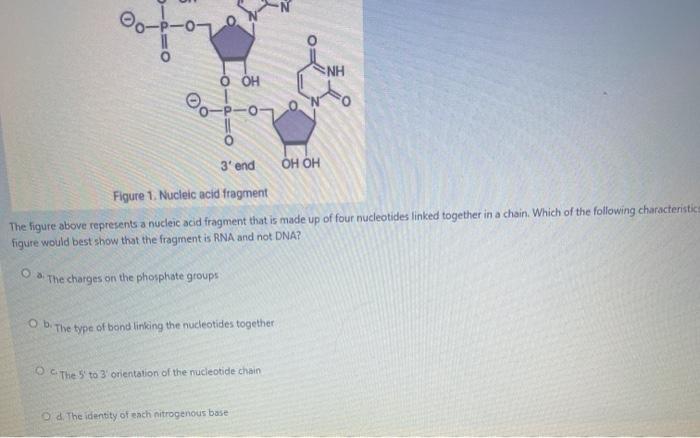
The amino acid sequences is controlled by the nucleotide codons of mRNA. The tertiary structure of a protein is the three-dimensional shape. The simplest level of protein structure primary structure is simply the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
CIt involves hydrogen bonding between amino acid side- chains. The sequence of amino acids in a protein the primary structure will determine where alpha helices and beta sheets the secondary structures will occure. Which of the following describes the tertiary structure of proteins.
The interactions between the side chains in a protein result into its tertiary structure. The secondary structure of a protein is formed due to hydrogen bonding present amino acid molecules. To some extent the tertiary structure is determined by the amino acid sequence of the primary structure.
Which of the following statements describes the tertiary structure of a protein. Click card to see definition. The insulin molecule shown here is cow insulin although its structure is similar to that of human insulin.
The polypetides chain that forms a 3-dimensional structure is called as secondary structure. Generally the information for protein structure is contained within the amino acid sequence of the protein itself. Yes alpha helix and beta sheets are secondary structures wand when peptide chains containing these structures fold again by virtue of bond formation Hydrogen bonds Hydrophobic interaction van-der-wall interactions ionic bonds and covalent bonds they form the 3D model of a protein that is termed as.
The Tertiary Structure of a protein is the arrangement of the secondary structures into this final 3-dimensional shape. KERATIN IS MADE UP OF TWO RIGHT HANDED HELICES BUT IT MAKES A LEFT HANDED COIL. Hydrophobic interactions greatly contribute to the folding and shaping of a.

Solved Which Of The Following Best Describes How Amino Acids Chegg Com

Solved Which Best Describes Protein Tertiary Structure A The Chegg Com


0 Comments